Network Technology in the Age of 5G
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant leap forward in network technology, promising to revolutionize connectivity, performance, and innovation across various sectors. As 5G networks roll out globally, they bring new opportunities and challenges that will shape the future of network infrastructure and services. This blog post explores the transformative impact of 5G on network technology, highlighting both the opportunities it presents and the challenges that organizations must address.
Opportunities Offered by 5G
1. Enhanced Network Performance
5G technology introduces substantial improvements in network performance compared to its predecessors. Key benefits include:
- Increased Speeds: 5G networks offer significantly higher data speeds, with potential peak rates exceeding 10 Gbps. This enables faster downloads, streaming, and data transfer.
- Lower Latency: 5G reduces latency to as low as 1 millisecond, enabling near-instantaneous communication and supporting real-time applications such as online gaming and augmented reality (AR).
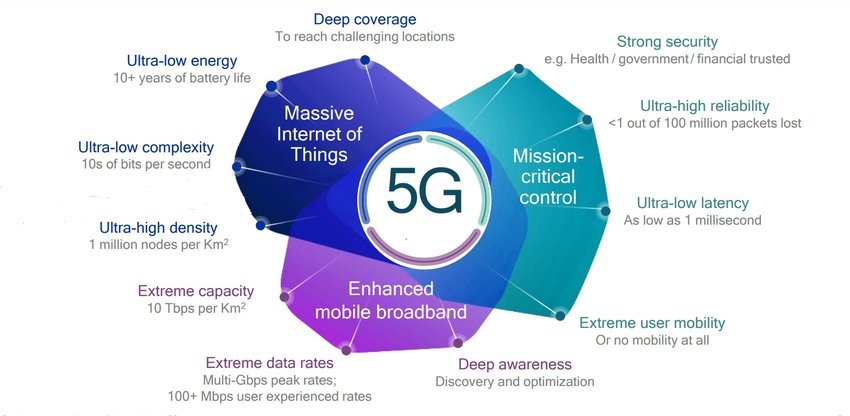
2. Greater Connectivity and Capacity
5G networks are designed to handle a vast number of connected devices and support a wide range of applications. Key aspects include:
- Massive IoT Support: 5G’s increased capacity allows for the seamless connection of millions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, driving innovations in smart cities, healthcare, and industrial automation.
- Improved Network Density: 5G’s advanced network architecture supports higher device density, ensuring reliable connectivity even in crowded environments.
3. New Business Opportunities
The deployment of 5G opens up new business opportunities across various industries:
- Smart Cities: 5G enables smart city initiatives by providing the infrastructure needed for connected sensors, intelligent transportation systems, and enhanced public services.
- Healthcare Innovation: 5G supports telemedicine and remote healthcare solutions by providing the bandwidth and low latency required for high-definition video consultations and real-time patient monitoring.
4. Enhanced User Experiences
5G technology enhances user experiences by enabling new and immersive applications:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): The high speeds and low latency of 5G enable seamless AR and VR experiences, transforming entertainment, education, and training applications.
- High-Definition Streaming: 5G supports high-definition and ultra-high-definition video streaming, improving the quality of content consumption for users.
Challenges of 5G Technology
1. Infrastructure Requirements
The deployment of 5G requires significant upgrades and investments in network infrastructure:
- Dense Network Deployment: 5G requires a higher density of cell sites and small cells to deliver optimal performance, which poses challenges in terms of installation, maintenance, and cost.
- Backhaul Upgrades: Enhancing network backhaul infrastructure is essential to support the increased data throughput and reduce bottlenecks in 5G networks.
2. Spectrum Management
Effective spectrum management is crucial for the successful deployment and operation of 5G networks:
- Spectrum Allocation: 5G operates across a range of spectrum bands, including low, mid, and high-frequency bands. Efficient allocation and management of these spectrum bands are necessary to ensure optimal coverage and performance.
- Regulatory Challenges: Navigating regulatory requirements and obtaining spectrum licenses can be complex and time-consuming, impacting the speed of 5G rollouts.
3. Security and Privacy Concerns
The deployment of 5G introduces new security and privacy challenges:
- Increased Attack Surface: The expansion of connected devices and networks creates a larger attack surface for potential cyber threats. Ensuring robust security measures is essential to protect against data breaches and malicious attacks.
- Privacy Issues: The collection and processing of vast amounts of data by 5G networks raise concerns about data privacy and the need for effective data protection measures.
4. Cost Considerations
The costs associated with deploying and maintaining 5G networks can be substantial:
- Investment in Infrastructure: Building and upgrading network infrastructure to support 5G requires significant capital investment, which may be a barrier for some organizations.
- Operational Costs: The ongoing operational costs of managing a 5G network, including energy consumption and maintenance, must be carefully managed to ensure long-term sustainability.
The Future of 5G and Network Technology
As 5G technology continues to evolve, its impact on network technology will shape the future of connectivity and innovation. Key trends and developments to watch include:
1. Integration with Edge Computing
The integration of 5G with edge computing will enhance network performance and support real-time data processing:
- Low-Latency Applications: Edge computing combined with 5G will enable ultra-low-latency applications, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Distributed Data Processing: Edge computing will support distributed data processing, reducing the need for data to travel long distances and improving efficiency.
2. Advancements in Network Slicing
Network slicing will enable the creation of virtual network segments tailored to specific applications and use cases:
- Customizable Network Services: Network slicing allows for the customization of network resources to meet the specific requirements of different applications, such as IoT, AR, and mission-critical communications.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Network slicing improves resource utilization by enabling the dynamic allocation of network capacity based on demand.
3. Emergence of 6G Technology
Looking ahead, research and development in 6G technology will pave the way for the next generation of wireless connectivity:
- Enhanced Capabilities: 6G will aim to provide even higher speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity compared to 5G, further advancing the possibilities for emerging technologies and applications.
Conclusion
The age of 5G technology presents significant opportunities and challenges for network technology. While 5G offers enhanced performance, greater connectivity, and new business opportunities, it also requires substantial investments in infrastructure, spectrum management, and security. As organizations navigate the complexities of 5G deployment, they must strategically address these challenges to fully realize the potential of this transformative technology. Looking ahead, the continued evolution of 5G and the emergence of future technologies will shape the future of network connectivity and innovation.