Best Practices for Managing and Securing Network Technology
- By -Mash
- Posted on
- Posted in Network Technology
Effective management and security of network technology are crucial for ensuring robust performance, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining operational continuity. As networks become increasingly complex and integral to business operations, adopting best practices for managing and securing network technology is essential. This article outlines key strategies for optimizing network performance and safeguarding against threats.
Network Management Best Practices
1. Regular Network Monitoring
Consistent monitoring of network performance is essential for detecting and addressing issues before they escalate. Implement network monitoring tools to track metrics such as bandwidth usage, latency, and packet loss. These tools provide real-time insights into network health and help identify potential problems, allowing for timely intervention and maintenance.
2. Implement Centralized Management
Centralized network management simplifies the administration of network resources, devices, and configurations. Use network management platforms to consolidate control over various network components, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. This approach enhances visibility, streamlines configuration management, and facilitates troubleshooting.
3. Establish Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to improve performance and security. Implement Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) to separate different types of traffic, such as guest access and internal applications. Segmentation limits the spread of network issues and enhances security by containing potential threats within specific segments.
4. Automate Routine Tasks
Automation tools can streamline routine network management tasks, such as configuration changes, updates, and backups. Implement automated scripts and workflows to reduce manual intervention, minimize errors, and ensure consistency in network operations. Automation also improves efficiency and allows IT staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
5. Perform Regular Updates and Patches
Keeping network devices and software up-to-date is critical for maintaining security and performance. Regularly apply firmware updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities and improve functionality. Develop a patch management strategy that includes testing updates in a controlled environment before deployment.
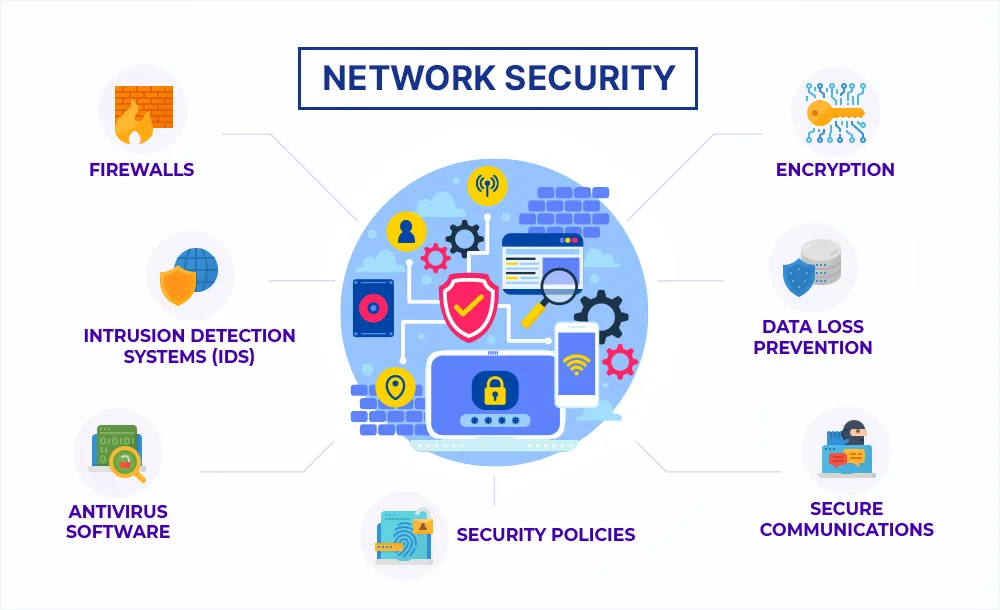
Network Security Best Practices
1. Implement Strong Access Controls
Restrict access to network resources based on user roles and responsibilities. Use access control lists (ACLs) and role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information and critical systems. Enforce strong password policies and require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for additional security.
2. Utilize Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Deploy firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to protect the network from external threats and unauthorized access. Firewalls monitor and filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules, while IDS systems detect and alert on suspicious activities and potential breaches.
3. Encrypt Data Transmission
Encrypt data transmitted over the network to protect it from interception and unauthorized access. Use encryption protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) for web traffic and Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) for VPN connections. Ensure that sensitive data, including personal and financial information, is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
4. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Perform regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of network security measures and identify potential vulnerabilities. Audits should include vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and reviews of security policies and procedures. Use audit findings to address weaknesses and enhance overall network security.
5. Develop an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines procedures for responding to and managing security incidents. Develop a comprehensive plan that includes steps for detecting, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security breaches. Regularly review and update the plan, and conduct simulated exercises to ensure readiness.
Ensuring Network Performance and Reliability
1. Optimize Network Configuration
Proper network configuration is essential for achieving optimal performance. Configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical traffic, such as VoIP and video conferencing, and minimize latency and jitter. Regularly review and adjust network configurations based on changing requirements and usage patterns.
2. Implement Redundancy and Failover Solutions
To ensure network reliability, implement redundancy and failover solutions. Use redundant network paths, devices, and power supplies to minimize the impact of hardware failures and network disruptions. Configure automatic failover mechanisms to switch to backup resources in case of primary system failures.
3. Scale Network Resources Appropriately
As network demands grow, it is important to scale network resources to maintain performance and avoid bottlenecks. Monitor network traffic and usage trends to anticipate capacity needs and plan for upgrades or expansions. Implement scalable solutions, such as cloud-based services and modular hardware, to accommodate future growth.
4. Educate Users on Best Practices
Educate employees about network security best practices and their role in maintaining a secure network environment. Provide training on recognizing phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious links, and following password management policies. Regular awareness programs help reduce the risk of human errors and enhance overall network security.
Conclusion
Managing and securing network technology involves a combination of best practices for performance optimization and threat protection. By implementing regular monitoring, centralized management, and strong access controls, organizations can ensure a reliable and secure network environment. Additionally, focusing on encryption, incident response, and user education further strengthens network security and resilience. As network technology continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and best practices will be essential for maintaining an effective and secure network infrastructure.



