How Telecommunications Infrastructure Supports Smart Cities
- By -Mash
- Posted on
- Posted in Telecommunications
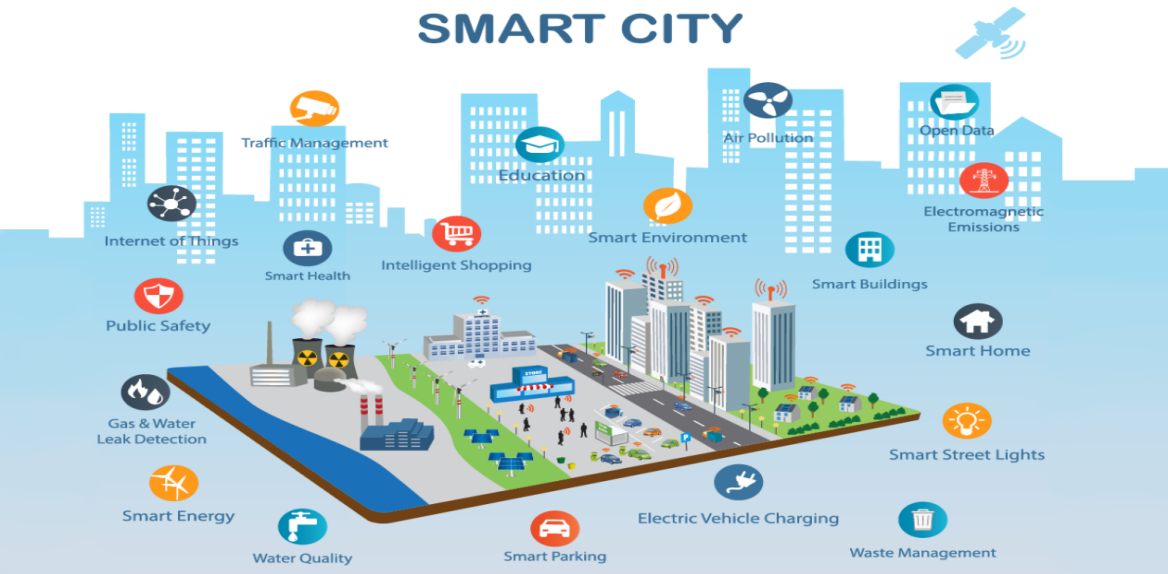
Smart cities leverage advanced technologies to enhance urban living through efficient resource management, improved public services, and better connectivity. Telecommunications infrastructure is a cornerstone of this transformation, providing the backbone for the connectivity and data exchange that enable smart city innovations. This article explores how telecommunications infrastructure supports smart cities and the benefits it brings to urban environments.
Enabling Connectivity and Integration
High-Speed Networks: Telecommunications infrastructure provides the high-speed networks necessary for the seamless operation of smart city systems. Fiber optics, 5G, and other advanced technologies offer the bandwidth and speed required to support the vast number of connected devices and sensors deployed throughout a smart city.
Wireless Communication: Wireless technologies, such as 5G and Wi-Fi, facilitate the connectivity of various smart city components, including traffic lights, environmental sensors, and public Wi-Fi hotspots. These technologies enable real-time data transmission and ensure that different systems can communicate effectively.
IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) is central to smart city functionality, with sensors and devices collecting data to monitor and manage urban systems. Telecommunications infrastructure supports IoT connectivity by providing the networks needed to transmit data from devices to central systems for processing and analysis.
Supporting Smart Infrastructure and Services
Smart Traffic Management: Telecommunications infrastructure enables smart traffic management systems that use real-time data to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve safety. Sensors and cameras collect data on traffic conditions, which is transmitted through telecommunications networks to traffic management centers for analysis and decision-making.
Public Safety and Surveillance: Smart cities use telecommunications networks to support public safety initiatives, including surveillance systems, emergency response coordination, and incident detection. High-definition cameras and sensors provide real-time data to law enforcement and emergency services, enhancing their ability to respond quickly to incidents.
Environmental Monitoring: Environmental sensors deployed throughout a smart city collect data on air quality, noise levels, and weather conditions. Telecommunications infrastructure ensures that this data is transmitted to central systems where it can be analyzed and used to make informed decisions about environmental policies and public health.
Enhancing Citizen Engagement and Services
Smart Public Services: Telecommunications infrastructure supports the delivery of smart public services, such as digital kiosks, e-governance platforms, and smart parking solutions. These services rely on robust connectivity to function effectively and provide citizens with convenient access to information and services.
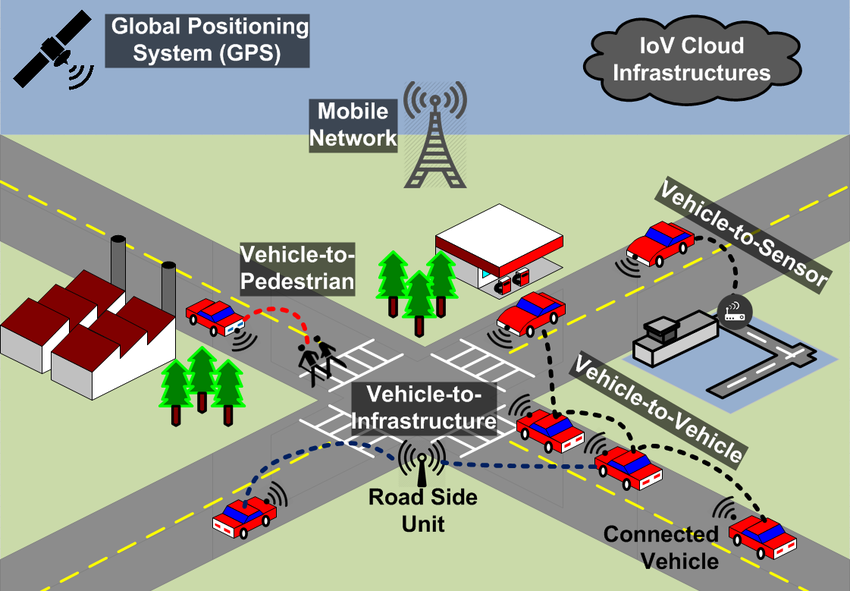
Connected Transportation: Smart cities use telecommunications networks to support connected transportation systems, including ride-sharing services, electric vehicle (EV) charging stations, and autonomous vehicles. These systems rely on real-time data and communication to operate efficiently and integrate with other smart city components.
Enhanced Communication Channels: Telecommunications infrastructure enables improved communication channels between city authorities and residents. Through mobile apps, social media, and digital platforms, citizens can report issues, access information, and engage with city services, leading to more responsive and transparent governance.
Driving Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy Management: Smart grids and energy management systems use telecommunications networks to monitor and control energy usage in real-time. By integrating renewable energy sources, optimizing energy distribution, and reducing waste, smart cities can achieve greater energy efficiency and sustainability.
Waste Management: Telecommunications infrastructure supports smart waste management systems that use sensors to monitor waste levels in bins and optimize collection routes. This approach reduces operational costs, minimizes environmental impact, and improves overall waste management efficiency.
Water Management: Smart water systems rely on telecommunications networks to monitor water usage, detect leaks, and manage irrigation. Real-time data collection and analysis enable better water resource management and conservation, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Success
Scalability: As smart cities expand and evolve, telecommunications infrastructure must be scalable to accommodate growing data traffic and increasing numbers of connected devices. Providers must invest in upgrading networks and implementing solutions that can handle future demands.
Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of data transmitted through telecommunications networks is crucial. Smart cities must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, secure authentication, and regular monitoring, to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Integration and Interoperability: Effective smart city deployment requires the integration and interoperability of various systems and technologies. Telecommunications infrastructure must support seamless communication between different components, ensuring that data flows efficiently and systems work together harmoniously.
Cost Management: The implementation and maintenance of telecommunications infrastructure for smart cities can be costly. Cities must carefully manage budgets, seek funding opportunities, and prioritize investments to balance the benefits of smart technologies with financial constraints.
Future Directions
5G and Beyond: The deployment of 5G technology is expected to further enhance smart city capabilities by providing even higher speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity. Future advancements, such as 6G, will continue to drive innovation and support new smart city applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning will play an increasingly important role in smart cities, enabling advanced data analysis, predictive analytics, and automation. Telecommunications infrastructure will support the integration of AI technologies into smart city systems.
Sustainable Practices: Future smart cities will focus on sustainability, integrating green technologies and practices into telecommunications infrastructure. This includes energy-efficient network equipment, renewable energy sources, and eco-friendly design principles.
Conclusion
Telecommunications infrastructure is essential to the development and success of smart cities. By providing the connectivity, data transmission, and integration needed for smart technologies, telecommunications enables efficient urban management, improved public services, and enhanced citizen engagement. As smart cities continue to evolve, telecommunications will play a pivotal role in driving innovation, addressing challenges, and creating more connected, sustainable, and efficient urban environments.