The Future of Networking: Software-Defined Networks (SDN)
As the digital landscape evolves, traditional networking approaches are giving way to more flexible and scalable solutions. Software-Defined Networks (SDN) represent a significant shift in how networks are managed and operated, offering enhanced control, agility, and efficiency. This blog post explores the future of networking with SDN, highlighting its benefits, architecture, and potential impact on modern IT infrastructures.
What is Software-Defined Networking (SDN)?
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is an approach to network management that separates the network control plane from the data plane. This separation allows network administrators to manage and configure network resources dynamically and centrally through software, rather than relying on traditional hardware-based configurations.
Key Benefits of SDN
SDN offers several advantages over traditional networking methods, making it a compelling choice for modern IT infrastructures:
1. Increased Flexibility
SDN provides greater flexibility by allowing network administrators to programmatically control network behavior. This flexibility enables rapid adjustments to network configurations, making it easier to respond to changing business needs and network conditions.
2. Enhanced Scalability
With SDN, networks can be scaled more easily and efficiently. Administrators can deploy and manage new network resources and services through software, reducing the need for manual hardware changes and enabling seamless scaling as demand grows.
3. Improved Network Management
SDN simplifies network management by centralizing control through a single software interface. This centralized approach provides a unified view of the network, making it easier to monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, and implement policy changes.
4. Cost Savings
By reducing the reliance on specialized hardware and streamlining network management processes, SDN can lead to significant cost savings. Organizations can lower operational costs through automation and minimize capital expenditures on network equipment.
5. Enhanced Security
SDN enhances network security by enabling more granular and dynamic control over network traffic. Administrators can implement security policies and respond to threats in real-time, improving the overall security posture of the network.
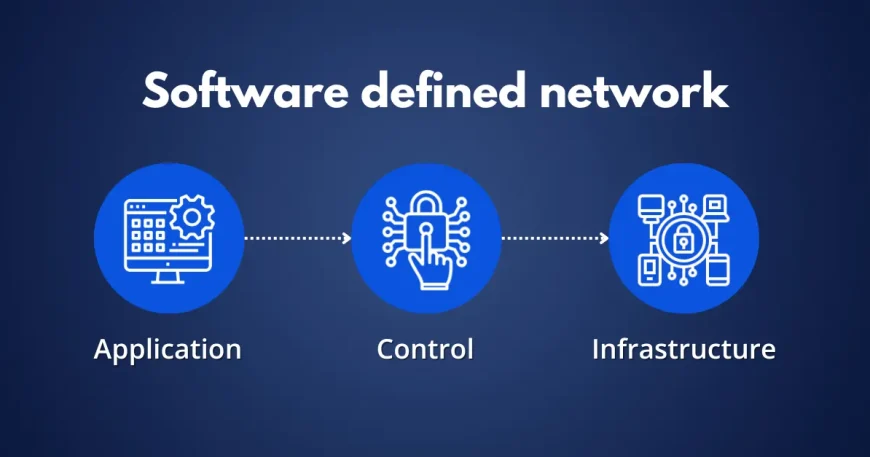
SDN Architecture
The architecture of SDN is designed to facilitate its flexible and programmable nature. It consists of three main components:
1. Data Plane
The data plane, also known as the forwarding plane, handles the actual transmission of data packets between devices. In SDN, the data plane remains largely unchanged from traditional networks but operates under the control of the SDN controller.
2. Control Plane
The control plane is responsible for managing network traffic and making decisions about how data should be routed. In SDN, the control plane is abstracted from the hardware and is implemented through software running on an SDN controller. This separation allows for centralized and programmable network control.
3. Application Plane
The application plane includes network applications and services that interact with the SDN controller. These applications leverage the SDN API to configure and manage network behavior, providing functions such as traffic management, network optimization, and security enforcement.
Implementing SDN: Best Practices
To successfully implement SDN, consider the following best practices:
1. Assess Network Requirements
Evaluate your current network infrastructure and identify areas where SDN can provide the most benefit. Consider factors such as network size, complexity, and specific use cases to determine the best approach for integration.
2. Choose the Right SDN Controller
Select an SDN controller that aligns with your network needs and supports the required features and protocols. Evaluate options based on scalability, performance, and compatibility with existing network components.
3. Plan for Integration
Develop a comprehensive integration plan to transition from a traditional network to an SDN-based architecture. Ensure that all stakeholders are involved and that potential challenges are addressed during the implementation process.
4. Train and Educate Staff
Provide training and education for network administrators and IT staff to ensure they are proficient in SDN concepts and technologies. Proper training will help maximize the benefits of SDN and ensure smooth operation.
5. Monitor and Optimize
Continuously monitor the performance of your SDN-enabled network and make adjustments as needed. Use network analytics and monitoring tools to gain insights into network behavior and optimize performance.
The Future of SDN
As technology continues to advance, SDN is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of networking. Innovations in network virtualization, automation, and artificial intelligence are expected to further enhance the capabilities of SDN, making networks more adaptive, intelligent, and efficient.
1. Integration with Cloud Computing
SDN will increasingly integrate with cloud computing environments, enabling more dynamic and flexible network management for cloud-based applications and services.
2. Adoption of Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
The convergence of SDN and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) will drive greater network agility and efficiency, allowing for the virtualization of network functions and services.
3. Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies will enhance SDN capabilities by enabling more intelligent network management, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making.
Conclusion
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) represents a transformative shift in network management, offering increased flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. By separating the control plane from the data plane, SDN enables centralized, programmable network control and enhances overall network performance. As organizations continue to adopt SDN and integrate it with emerging technologies, the future of networking will be characterized by greater agility, intelligence, and innovation.



