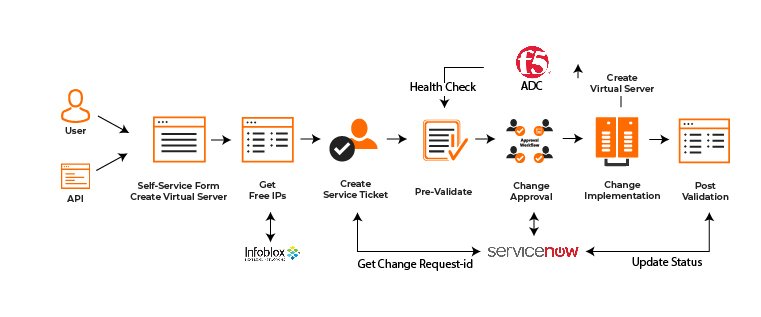
How to Implement Network Automation in Your IT Infrastructure
Network automation is transforming the way IT infrastructures are managed, offering increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved network performance. By automating routine tasks and processes, organizations can streamline network management, minimize human errors, and respond more quickly to changing conditions. This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to implementing network automation in your IT infrastructure, including key strategies, tools, and best practices.
Key Benefits of Network Automation
Before diving into the implementation process, it’s important to understand the benefits that network automation can bring to your IT infrastructure:
1. Increased Efficiency
Automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as network configuration and monitoring, frees up valuable time for IT staff. This allows them to focus on more strategic initiatives and reduces the need for manual intervention.
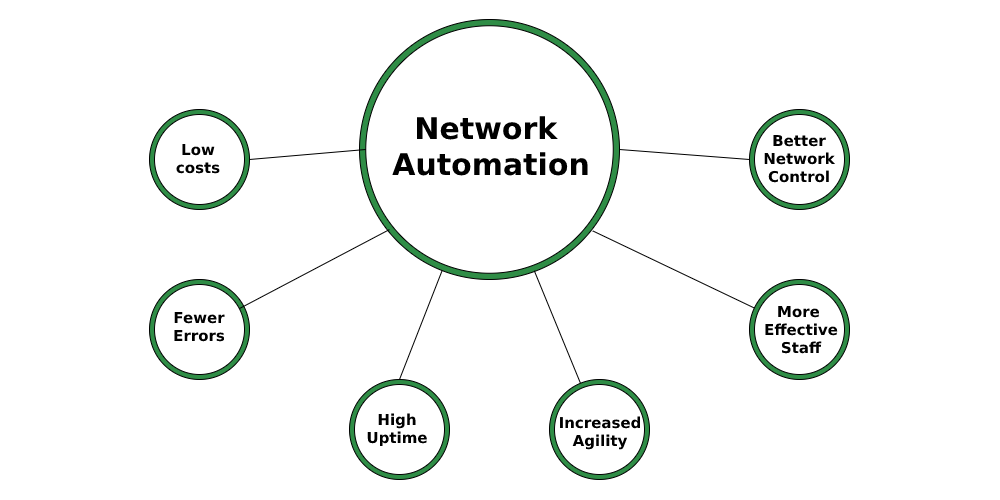
2. Reduced Human Error
Manual network management is prone to human errors, which can lead to misconfigurations and downtime. Automation reduces the risk of errors by executing predefined tasks with precision and consistency.
3. Improved Network Performance
Automation enables real-time adjustments and optimizations, enhancing overall network performance. Automated tools can monitor network conditions and make adjustments to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
4. Enhanced Scalability
As your network grows, automation simplifies the process of scaling network resources and managing complex configurations. This ensures that your IT infrastructure can accommodate increased demands without additional manual effort.
Steps to Implement Network Automation
1. Assess Your Current Network Infrastructure
Before implementing automation, conduct a thorough assessment of your existing network infrastructure. Identify the tasks and processes that can benefit from automation, such as:
- Network configuration and provisioning
- Performance monitoring and alerting
- Security management and compliance
- Incident response and troubleshooting
2. Define Clear Objectives and Goals
Establish clear objectives and goals for your network automation initiative. Consider factors such as:
- Efficiency Improvements: Identify areas where automation can reduce manual effort and improve operational efficiency.
- Error Reduction: Set goals for minimizing human errors and ensuring consistent network configurations.
- Performance Optimization: Define performance metrics and targets for automated adjustments and optimizations.
3. Choose the Right Automation Tools
Select automation tools and platforms that align with your network automation objectives and requirements. Key considerations include:
- Network Automation Platforms: Tools such as Cisco DNA, Ansible, and Puppet provide comprehensive automation capabilities for network management.
- Configuration Management Tools: Tools like SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager and ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager assist with automating network configurations and change management.
- Monitoring and Analytics Tools: Tools such as PRTG Network Monitor and Splunk provide real-time monitoring and analytics to support automated decision-making.
4. Develop and Test Automation Scripts
Create and test automation scripts to perform specific network tasks. Key practices include:
- Script Development: Write scripts to automate tasks such as network provisioning, configuration changes, and performance monitoring.
- Testing: Thoroughly test scripts in a controlled environment to ensure they perform as expected and do not introduce unintended issues.
5. Implement Automation in Phases
Implement network automation gradually to minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth transition. Key phases include:
- Pilot Testing: Begin with a pilot phase to test automation tools and scripts in a limited scope. Monitor performance and gather feedback to refine the implementation.
- Gradual Rollout: Gradually expand automation to additional network components and tasks based on the success of the pilot phase.
6. Monitor and Optimize Automated Processes
Once automation is in place, continuously monitor and optimize automated processes to ensure they meet performance and reliability goals. Key practices include:
- Performance Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track the performance of automated processes and identify any issues or inefficiencies.
- Regular Updates: Update and refine automation scripts and tools based on feedback and changes in network requirements.
7. Train and Educate IT Staff
Ensure that IT staff are trained and educated on network automation tools and processes. Key training areas include:
- Tool Usage: Provide training on how to use automation tools and platforms effectively.
- Troubleshooting: Educate staff on troubleshooting automated processes and resolving any issues that may arise.
Best Practices for Network Automation
1. Start with Simple Tasks
Begin with automating simple and repetitive tasks to build confidence and demonstrate the value of automation. Gradually expand to more complex processes as you gain experience.
2. Ensure Proper Documentation
Document automation scripts, processes, and configurations to facilitate management and troubleshooting. Clear documentation helps maintain consistency and supports future updates.
3. Maintain Flexibility
Design automation processes to be flexible and adaptable to changing network conditions and requirements. This ensures that automation can continue to provide value as your network evolves.
4. Implement Security Best Practices
Ensure that automation processes follow security best practices to prevent vulnerabilities and protect sensitive data. Regularly review and update security policies related to automation.
Conclusion
Implementing network automation in your IT infrastructure offers significant benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved performance. By assessing your current infrastructure, defining clear objectives, choosing the right tools, and following best practices, you can successfully automate network management tasks and enhance your overall network operations. Embrace network automation as a strategic initiative to drive greater agility, scalability, and reliability in your IT infrastructure.