How to Respond to a Security Breach
A security breach can have significant implications for your organization, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal consequences. Responding effectively to a breach is crucial to minimize damage and recover swiftly. This blog post provides a comprehensive guide on incident management and recovery, outlining key steps, best practices, and tools for handling and recovering from a security breach.
Steps to Respond to a Security Breach
1. Detection and Identification
Monitor for Signs of a Breach
Continuous monitoring of your IT environment helps detect anomalies and potential breaches early. Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools to identify unusual activities.
Verify the Breach
Once a potential breach is detected, verify its authenticity. Determine the scope, impact, and nature of the breach by analyzing logs, alerts, and any affected systems. Confirm whether it’s a genuine security incident or a false alarm.
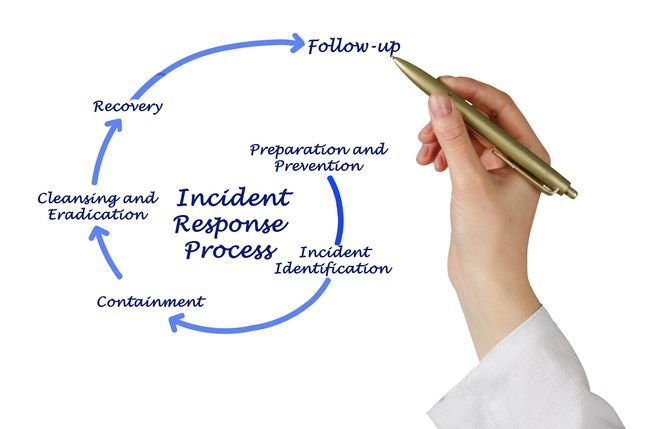
2. Containment
Isolate Affected Systems
Immediately isolate affected systems to prevent further spread of the breach. Disconnect compromised devices from the network and restrict access to sensitive data to contain the incident.
Implement Temporary Measures
Apply temporary security measures to limit the impact of the breach. This may include disabling compromised accounts, blocking malicious IP addresses, and halting unauthorized data transfers.
3. Eradication
Remove the Threat
Identify and eliminate the root cause of the breach. This involves removing malware, closing vulnerabilities, and addressing any weaknesses that allowed the breach to occur.
Patch and Update Systems
Apply security patches and updates to affected systems to prevent similar breaches in the future. Ensure that all software and hardware are up-to-date with the latest security fixes.
4. Recovery
Restore Systems and Data
Begin the process of restoring affected systems and data from backups. Ensure that backups are clean and free from malware before restoring them to the production environment.
Monitor for Residual Issues
Continuously monitor systems after recovery to detect any residual issues or potential reoccurrences of the breach. Implement additional security measures if necessary to enhance protection.
5. Communication
Notify Stakeholders
Communicate with key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners, about the breach. Provide clear and accurate information on the impact, response efforts, and any actions required from them.
Report to Authorities
Report the breach to relevant regulatory authorities and law enforcement agencies as required by laws and regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA. Ensure compliance with breach notification requirements.
6. Post-Incident Analysis
Conduct a Post-Mortem Review
Perform a thorough post-incident review to analyze the breach’s causes, impact, and response effectiveness. Identify lessons learned and areas for improvement in your incident response plan.
Update Incident Response Plan
Revise and update your incident response plan based on the insights gained from the breach. Incorporate new procedures, tools, and best practices to enhance your readiness for future incidents.
Best Practices for Incident Management and Recovery
1. Develop a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
- Create a Response Team: Assemble a dedicated incident response team with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Establish Procedures: Develop clear procedures for detecting, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security breaches.
- Regularly Test the Plan: Conduct regular drills and simulations to test the effectiveness of your incident response plan.
2. Implement Strong Security Controls
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance security by requiring multiple forms of verification for accessing sensitive systems and data.
- Maintain Up-to-Date Security Measures: Regularly update and patch systems, applications, and security tools to protect against vulnerabilities and threats.
3. Conduct Regular Security Audits
- Evaluate Security Posture: Perform regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of your security controls and identify potential weaknesses.
- Address Findings: Implement recommendations and improvements based on audit findings to strengthen your security posture.
4. Provide Employee Training
- Educate Staff: Train employees on recognizing and reporting security incidents, following best practices for data protection, and understanding their role in incident response.
- Promote Security Awareness: Foster a culture of security awareness to reduce the risk of human error and insider threats.
5. Invest in Threat Detection Tools
- Deploy Monitoring Solutions: Use IDS, SIEM, and other monitoring tools to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time.
- Leverage Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities to proactively address potential risks.
Conclusion
Responding to a security breach requires a well-coordinated approach to incident management and recovery. By following key steps—detection, containment, eradication, recovery, communication, and post-incident analysis—you can effectively manage and mitigate the impact of a breach. Implementing best practices, developing a comprehensive incident response plan, and investing in security technologies are essential for protecting your organization from future incidents and ensuring a swift recovery.