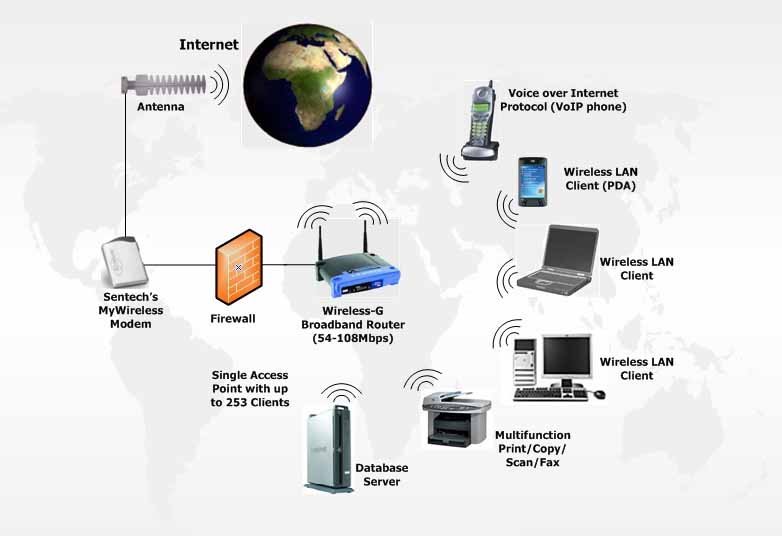
Advances in Wireless Network Technology: What You Need to Know
- By -Mash
- Posted on
- Posted in Network Technology
Wireless network technology is evolving rapidly, driving advancements that enhance connectivity, speed, and efficiency. As businesses and consumers increasingly rely on wireless solutions, staying informed about these advances is crucial for leveraging the latest capabilities and optimizing network performance. This article explores the key developments in wireless network technology and their implications for various applications.

Emerging Wireless Standards
5G Technology: 5G represents a significant leap forward from previous wireless standards, offering higher speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity. This technology supports faster data transfer rates, enabling seamless streaming, real-time communication, and advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). 5G’s low latency is particularly beneficial for applications requiring near-instantaneous responses, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries.
Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E: Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 6E are the latest advancements in Wi-Fi technology, offering improved performance in high-density environments. Wi-Fi 6 provides faster speeds, increased capacity, and better efficiency by utilizing advanced features such as Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Target Wake Time (TWT). Wi-Fi 6E extends these benefits to the 6 GHz band, offering additional spectrum for reduced congestion and enhanced performance.
Enhanced Network Efficiency
Beamforming: Beamforming technology focuses the wireless signal directly towards the connected device, rather than broadcasting it in all directions. This targeted approach improves signal strength and coverage, resulting in faster speeds and better performance. Beamforming is particularly useful in environments with many obstacles or interference, such as office buildings and urban areas.
MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output): MU-MIMO technology allows a wireless access point to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, rather than sequentially. This capability enhances network efficiency and reduces latency, improving the overall user experience, especially in environments with numerous connected devices.
Network Slicing: Network slicing enables the creation of multiple virtual networks within a single physical network infrastructure. Each slice operates independently, allowing for customized services and optimized performance based on specific needs. This technology is particularly beneficial for 5G networks, where different applications may require varying levels of speed, latency, and reliability.
Expanding Spectrum and Capacity
Spectrum Utilization: Advances in wireless network technology include the utilization of additional spectrum bands to increase capacity and reduce congestion. The allocation of new frequency bands, such as the 6 GHz band for Wi-Fi 6E, provides more bandwidth for high-speed and high-capacity applications.
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing: Dynamic spectrum sharing allows multiple wireless technologies to coexist in the same frequency band. This approach maximizes the use of available spectrum and improves network efficiency by dynamically allocating resources based on real-time demand. Dynamic spectrum sharing is a key feature of 5G networks, enabling coexistence with existing technologies like 4G LTE.
Enhanced Security Measures
Advanced Encryption: The latest wireless standards incorporate stronger encryption protocols to protect data transmitted over the network. For example, WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) provides enhanced security features, such as improved protection against brute-force attacks and better encryption for open networks.
Security Protocols for 5G: 5G networks introduce advanced security measures, including enhanced encryption, authentication, and privacy features. These protocols address the increased risks associated with the expanded attack surface of 5G networks and provide robust protection for sensitive data and communications.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Internet of Things (IoT): Wireless network advancements support the growing number of IoT devices by providing the necessary connectivity and bandwidth. Technologies like 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are designed to handle the increased data traffic and device density associated with IoT deployments, enabling seamless communication and data exchange.
Edge Computing: Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source, complements advancements in wireless technology by reducing latency and improving response times. This integration enhances the performance of applications that rely on real-time data processing, such as smart cities and industrial automation.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are increasingly integrated into wireless networks to optimize performance, predict network issues, and automate management tasks. These technologies enable intelligent network management, adaptive quality of service, and proactive maintenance, improving overall network efficiency and reliability.
Future Trends and Considerations
6G Development: Research and development efforts are already underway for 6G technology, which is expected to further revolutionize wireless networks. While still in the early stages, 6G promises even higher speeds, ultra-low latency, and advanced capabilities such as holographic communication and advanced AI integration.
Sustainability: As wireless technology advances, there is a growing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of network infrastructure include developing energy-efficient hardware, optimizing network operations, and incorporating renewable energy sources.
Regulatory and Standards Evolution: The evolution of wireless technology is accompanied by changes in regulations and standards. Staying informed about these developments is essential for ensuring compliance and leveraging the latest advancements effectively.
Conclusion
Advances in wireless network technology are driving significant improvements in connectivity, efficiency, and security. From emerging standards like 5G and Wi-Fi 6 to enhanced network efficiency and spectrum utilization, these developments are shaping the future of wireless communication. By understanding and adopting these technologies, businesses and consumers can optimize their network performance and stay ahead in an increasingly connected world.